ROI: How to calculate return on investment
Business administration offers various profitability metrics. One of the most important indicators of this type is the return on investment (ROI). The return on investment measures the profitability of the capital employed.
- Free Wildcard SSL for safer data transfers
- Free private registration for more privacy
- Free 2 GB email account
What is ROI? Its meaning
The return on investment is one of the most important metrics in accounting. It refers to the profit of a business entity (e.g., a company) in relation to the capital invested. Alternatively, ROI is also known as capital yield or capital profitability.
The significance of ROI is immense, as it sits at the top of the DuPont model, making it the centerpiece of the world’s oldest business performance measurement system. This model was introduced in 1919 by the American chemical company E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co..
Where is ROI used?
Within the DuPont indicator pyramid, ROI serves as a key metric for evaluating a company’s performance while considering the total capital investment. This value helps answer the question: How efficiently was the capital invested during the given accounting period?
In principle, however, ROI can be used as a performance indicator in any scenario where success is measured by the return on invested capital. Additional areas of application include:
- The evaluation of investments
- The comparison of investment projects
- The analysis of individual business divisions
How to calculate the ROI
Which indicators you apply to calculating your ROI value depends on whether you are determining your entire company’s rate of return for a particular accounting period or whether you simply want to calculate returns from single investments or a specific business division.
The ROI formula
According to the DuPont model, your company’s ROI is calculated by multiplying its return on sales by its asset turnover.

Alternatively, you can also calculate a company or investment’s ROI by dividing the profit by the total invested capital and multiplying the result by 100.

Both formulas produce the same result. This can be understood with the help of the following calculation.
Formula for calculation return on sales

With the return on sales, you determine your company’s share of the return on sales from the net sales.
Formula for calculating asset turnover
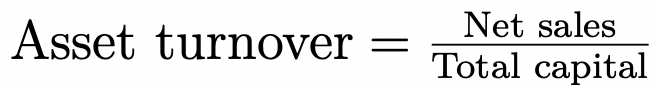
Asset turnover provides information on your company’s profit ratio with respect to the total assets (equity + debt capital).
Formula for calculating ROI
In the DuPont indicator pyramid, the return on sales and asset turnover are located directly under the return on investment situated at the top. This is illustrated in the following graphic.

Example for calculating ROI
Below we use an example to explain the calculation of ROI. For this we begin by assuming that a company has the following figures for the accounting period under consideration.
| Net sales | 45.5 million dollars |
|---|---|
| Total capital | 20.3 million dollars |
| Profit (before interest) | 2.8 million dollars |
To understand how to calculate ROI, we first determine the company’s return on sales. This is done by dividing the profit by net sales and multiplying the result by 100 to obtain a percentage. For the example company, the return on sales is 6.15%.

In the second step, we calculate the asset turnover. This is done by dividing the net sales by the total capital. For the example company, the capital turnover is 2.24.

By multiplying the return on sales by the asset turnover, we obtain an ROI of 13.8% for the given accounting period.

We obtain the same result when calculating ROI using the alternative method.

How to calculate the ROI of a single investment
If you don’t want to determine your entire company’s asset turnover but would rather determine the profitability of a single investment or that of a specific business division, then follow these instructions.
Divide the investment or business division’s profit share by the respective investment and multiply the result by 100.

These types of calculations are used in online marketing, for example, in order to figure out the success of advertising costs in relation to the profit they generate. In this context, it is referred to specifically as the return on marketing investment (ROMI).
Google recommends that website operators measure the success of advertising expenditures for Ad advertisements by using the ROI it generates. The following example shows how to do this.
Imagine that you operate an online store and that you advertise your products in the search engine. For the purchase of articles, you incur a cost of 2,500 dollars which you use to generate 4,000 dollars in sales. The Ad advertisements incur an expense of 500 dollars.
You can calculate the success of your marketing investments by dividing the profit share by these advertising costs and multiplying the result by 100. To do this, you can use the ROAS formula (return on advertising spend). It generates a ROI that refers to a specific profit share and the advertising costs that were spent to obtain it.

An ROAS of 200% is the result for this example.

Differentiation from other profitability indicators
As the top indicator of the DuPont model, return on investment (ROI) includes both the return on equity (ROE) and the return on assets (ROA), which consists of equity and debit capital.
Return on investment (ROI)

Return on Equity (ROE)

Return on assets (ROA)

How to interpret the ROI
Return on investment sheds light on the profitability of fixed capital. It can involve a company’s entire capital or the capital expenditure for a single investment.
The ROI is a measurement of this capital’s return. How you evaluate an ROI figure in the long run depends heavily on the sector in which the company is active or makes investments. Many business professionals aim for a return on investment that is more than 10 percent. On average, however, higher ROI values are obtained in commerce than industry. Within a company, determining the ROI value provides an opportunity to compare various investment projects or business divisions in terms of their profitability.
Criticism of ROI
Calculating ROI is considered one of the standard procedures for evaluating investment projects, both in forecasts and in the subsequent performance review. The indicator is quickly determined and also implies reproducibility. When it comes to describing financial implications, however, the ROI itself has limited informative value: when considering individual cases, repercussions within the overall context can fall by the wayside. Flaws emerge both in the analysis of the company’s overall results as well as in the evaluation of single investments.
- ROI is a book-value based indicator that generally only allows conclusions to be drawn about the past. ROI is not suitable for evaluating future investment projects.
- Investment risks and external influence factors aren’t taken into consideration when using ROI. These include economic and market risks, customer satisfaction, and competition.
- As ROI refers to a specific period under consideration, it is difficult to compare investments with varying terms. Furthermore, it isn’t always possible in practice to clearly match a company’s sales and profits to specific investment projects.
With the ROI, you determine the return on invested capital based on the company figures that are available to you. The profitability of future investment projects cannot be reliably determined using the ROI.
Please note the legal disclaimer for this article.